Extra Bone In Foot Accessory Navicular
Overview
The navicular bone of the foot is one of the small bones on the mid-foot. The bone is located at the instep, the arch at the middle of the foot. One of the larger tendons of the foot, called the posterior tibial tendon, attaches to the navicular before continuing under the foot and into the forefoot. This tendon is a tough band of tissue that helps hold up the arch of the foot. If there is an accessory navicular, it is located in the instep where the posterior tibial tendon attaches to the real navicular bone.

Causes
Like all painful conditions, ANS has a root cause. The cause could be the accessory navicular bone itself producing irritation from shoes or too much activity. Often, however, it is related to injury of one of the structures that attach to the navicular bone. Structures that attach to the navicular bone include abductor hallucis muscle, plantar calcaneonavicular ligament (spring ligament) parts of the deltoid ligament, posterior tibial tendon.
Symptoms
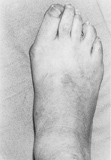
Most people born with this bone begin to experience the symptoms (if at all any) in adolescence. Some may not develop any symptoms until adulthood. The symptoms are a visible abnormal protrusion in the mid-foot, swelling and redness of the protrusion, pain in the mid-foot after performing an activity.
Diagnosis
It is important to examine the posterior tibial tendon and measure the extent of pain to this tendon proximal to the navicular bone. You can clinically determine the amount of posterior tibial tendon involvement by assessing the degree of swelling, pain on palpation and strength. To evaluate the patient?s strength, have the patient stand and balance on one foot along with rising up on his or her toes.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment of the accessory navicular begins with rest, which may include activity modification or temporary immobilization in a boot or a brace. Once the inflammation subsides the foot needs to be supported. The support consists of a specially designed orthotic arch support. Occasionally, the orthotic will dig into the edge of the accessory navicular bone under the arch of the foot. This is very uncomfortable. For this reason the orthotic support needs to be carefully made. The orthotic support will help control (but not cure) the flat foot and will often decrease the inflammation on the navicular.
Surgical Treatment
Fusion of the accessory navicular to the navicular with screws is required when there is a large accessory navicular bone and removal of this bone would reduce the articular surface of the Navicular to the talus (coxa pedis). Fusion will relieve pain without disrupting the tibialis posterior tendon insertion nor narrowing talar head support. In most instances, a patient’s recovery will be as follows. 0-6 weeks: Immobilization (in case or cast boot) non-weight-bearing or touch weight-bearing. 6-10 weeks: Increasing activity in a cast boot. Physical therapy to work on strength and balance. Full recovery after 9 weeks-2 months. In some patients (where the posterior tibial tendon is still intact and functioning) the treating surgeon may allow weight-bearing as tolerated in a cast boot immediately after surgery.
The navicular bone of the foot is one of the small bones on the mid-foot. The bone is located at the instep, the arch at the middle of the foot. One of the larger tendons of the foot, called the posterior tibial tendon, attaches to the navicular before continuing under the foot and into the forefoot. This tendon is a tough band of tissue that helps hold up the arch of the foot. If there is an accessory navicular, it is located in the instep where the posterior tibial tendon attaches to the real navicular bone.

Causes
Like all painful conditions, ANS has a root cause. The cause could be the accessory navicular bone itself producing irritation from shoes or too much activity. Often, however, it is related to injury of one of the structures that attach to the navicular bone. Structures that attach to the navicular bone include abductor hallucis muscle, plantar calcaneonavicular ligament (spring ligament) parts of the deltoid ligament, posterior tibial tendon.
Symptoms
Most people born with this bone begin to experience the symptoms (if at all any) in adolescence. Some may not develop any symptoms until adulthood. The symptoms are a visible abnormal protrusion in the mid-foot, swelling and redness of the protrusion, pain in the mid-foot after performing an activity.
Diagnosis
It is important to examine the posterior tibial tendon and measure the extent of pain to this tendon proximal to the navicular bone. You can clinically determine the amount of posterior tibial tendon involvement by assessing the degree of swelling, pain on palpation and strength. To evaluate the patient?s strength, have the patient stand and balance on one foot along with rising up on his or her toes.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment of the accessory navicular begins with rest, which may include activity modification or temporary immobilization in a boot or a brace. Once the inflammation subsides the foot needs to be supported. The support consists of a specially designed orthotic arch support. Occasionally, the orthotic will dig into the edge of the accessory navicular bone under the arch of the foot. This is very uncomfortable. For this reason the orthotic support needs to be carefully made. The orthotic support will help control (but not cure) the flat foot and will often decrease the inflammation on the navicular.

Surgical Treatment
Fusion of the accessory navicular to the navicular with screws is required when there is a large accessory navicular bone and removal of this bone would reduce the articular surface of the Navicular to the talus (coxa pedis). Fusion will relieve pain without disrupting the tibialis posterior tendon insertion nor narrowing talar head support. In most instances, a patient’s recovery will be as follows. 0-6 weeks: Immobilization (in case or cast boot) non-weight-bearing or touch weight-bearing. 6-10 weeks: Increasing activity in a cast boot. Physical therapy to work on strength and balance. Full recovery after 9 weeks-2 months. In some patients (where the posterior tibial tendon is still intact and functioning) the treating surgeon may allow weight-bearing as tolerated in a cast boot immediately after surgery.